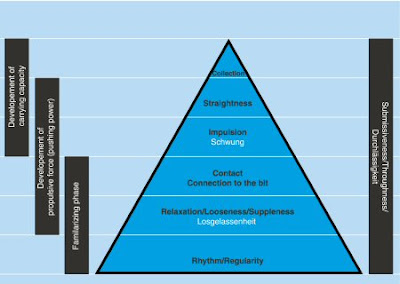
There are six building blocks of the German Training Scale. The German words for these scales have a more encompassing meaning than their vague English counterparts. The dressage training scale is often arranged in a pyramid or sequential fashion, with “rhythm and regularity” at the start of the pyramid and “collection” at the end. The training scale is helpful and effective as a guide for the training of any horse, but has come to be most closely associated with dressage. They are interdependant and interwoven each stage should be achieved before moving on to the next. They are not, however, a checklist of success. The lower rungs should always be revisited to check that progress is genuine and that the horse is fulfilling all the preceding requirements.
Rhythm and Regularity (Takt): Rhythm, gait, tempo, and regularity should be the same on straight and bending lines, through lateral work, and through transitions. Rhythm refers to the sequence of the footfalls, which should only include the pure walk, pure trot, and pure canter. The regularity, or purity, of the gait includes the evenness and levelness of the stride. Once a rider can obtain pure gaits, or can avoid irregularity, the combination may be fit to do a more difficult exercise.
Relaxation (Losgelassenheit): The second level of the pyramid is relaxation (looseness). Signs of looseness in the horse may be seen by an even stride that is swinging through the back and causing the tail to swing like a pendulum, looseness at the poll, a soft chewing of the bit, and a relaxed blowing through the nose. The horse makes smooth transitions, is easy to position from side to side, and willingly reaches down into the contact as the reins are lengthened.
Contact (Anlehnung): Contact—the third level of the pyramid—is the result of the horse’s pushing power, and should never be achieved by the pulling of the rider’s hands. The rider encourages the horse to stretch into soft hands that allow the horse to lift the base of the neck, coming up into the bridle, and should always follow the natural motion of the animal’s head. The horse should have equal contact in both reins.
Impulsion (Schwung): The pushing power (thrust) of the horse is called impulsion, and is the fourth level of the training pyramid. Impulsion is created by storing the energy of engagement. Proper impulsion is achieved by means of Correct driving aids of the rider,Throughness (Durchlässigkeit - the flow of energy through the horse from front to back and back to front) and Relaxation of the horse. Impulsion can occur at the walk, trot and canter. It is highly important to establish good, forward movement and impulsion at the walk, as achieving desirable form in the trot and canter relies heavily on the transition from a good, supple, forward walk.
Straightness (Geraderichtung): A horse is straight when the hind legs follow the path of the front legs, on both straight lines and on bending lines, and the body follows the line of travel. Straightness allows the horse to channel its impulsion directly toward its center of balance, and allows the rider’s hand aids to have a connection to the hind end.
Collection (Versammlung): At the apex of the training scale stands collection. It may refer to collected gaits: they can be used occasionally to supplement less vigorous work. It involves difficult movements (such as flying changes) in more advanced horses. Collection requires greater muscular strength, so must be advanced upon slowly. When in a collected gait, the stride length should shorten, and the stride should increase in energy and activity. When a horse collects, more weight moves to the hindquarters. Collection is natural for horses and is often seen during pasture play. A collected horse is able to move more freely. The joints of the hind limbs have greater flexion, allowing the horse to lower the hindquarters, bringing the hind legs further under the body, and lighten and lift the forehand. In essence, collection is the horse's ability to move its centre of gravity to the rear.
No comments:
Post a Comment